PRS19: Fret Press Robot
Unknown
In the last semester of my Master's degree, I took part in the Mechanical Engineering Master's Design Project (EN.530.614). Essentially Mechanical Engineering Senior Design with expanded scope and difficulty, the course is a year-long design project where students design, fabricate, and test solutions for sponsor companies' design problems. I joined the Paul Reed Smith (PRS) team near the end of the project, and developed the entire software suite for running their automatic fret press robot.
Background
Paul Reed Smith Guitars manufactures guitars largely by hand, making use of automated techniques when it is possible to maintain quality. One particular process they were interested in automating was that of gluing and pressing frets into the guitar neck—for each fret, a precise quantity of glue needs to be laid down in the fret slot, followed by placing and then pressing a fret on top. The task itself is somewhat intricate, but also incredibly repetitive, leading to burnout among employees performing it.
In 2018, PRS sponsored a JHU Senior Design team to design and build a robot for automating the process. Ultimately the scope of the project was too much to be completed in a single year, so PRS extended the project into 2019, and JHU Mechanical Engineering had a small team of Master's students take over its completion. I joined the Master's team during the final semester of the project, and was tasked with writing the entirety of the software needed to control and operate the robot.
Robot Design
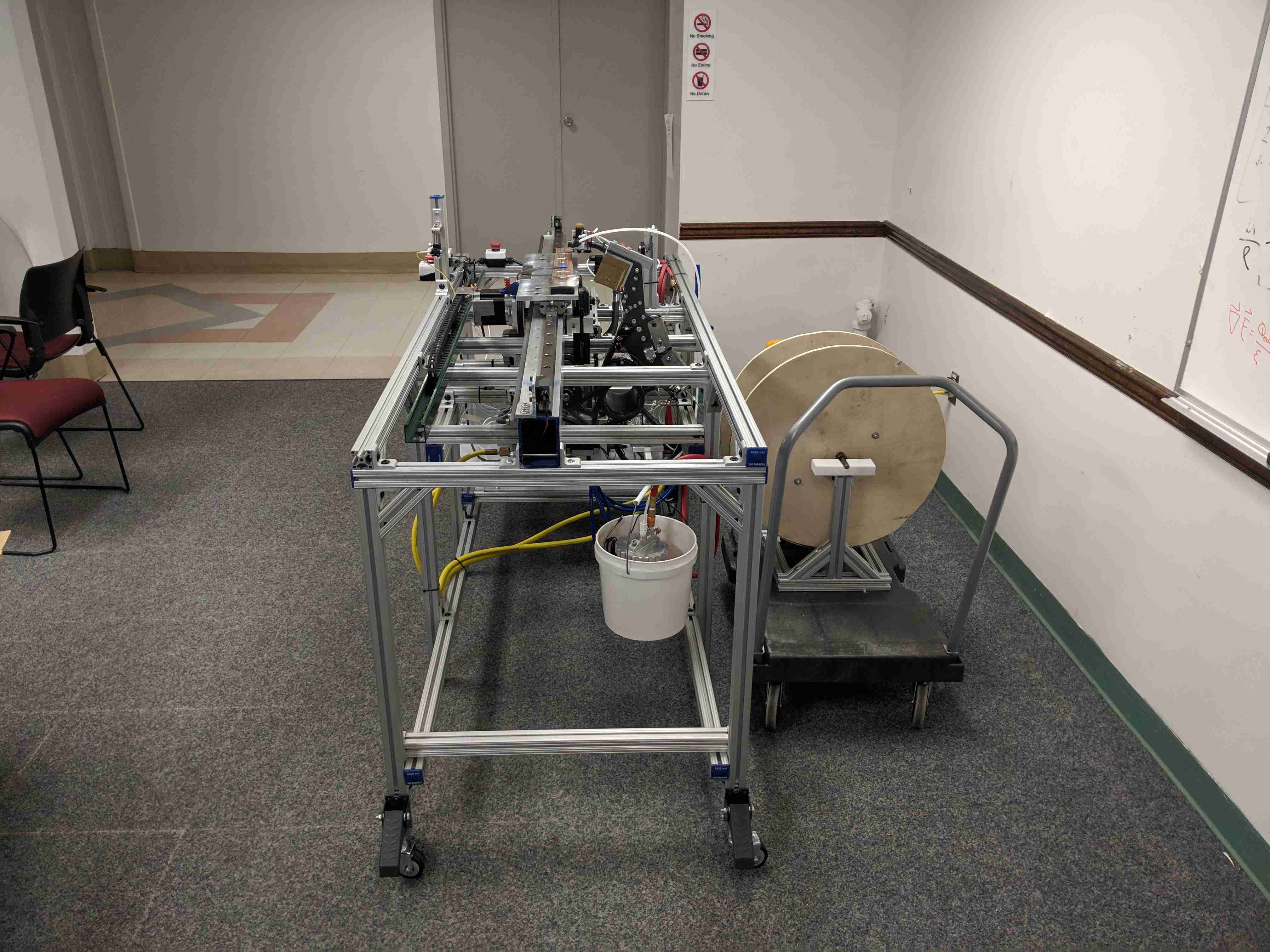
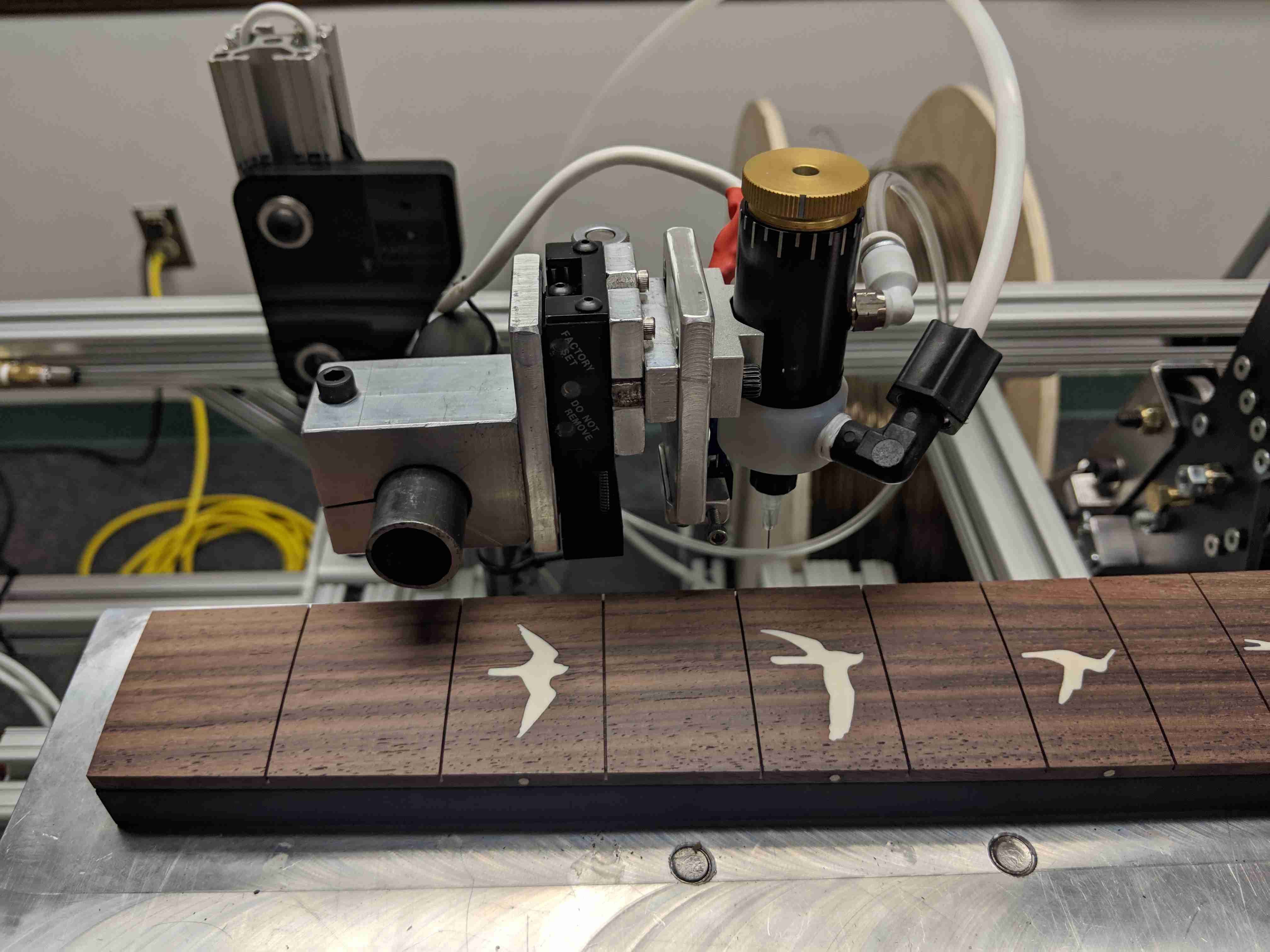
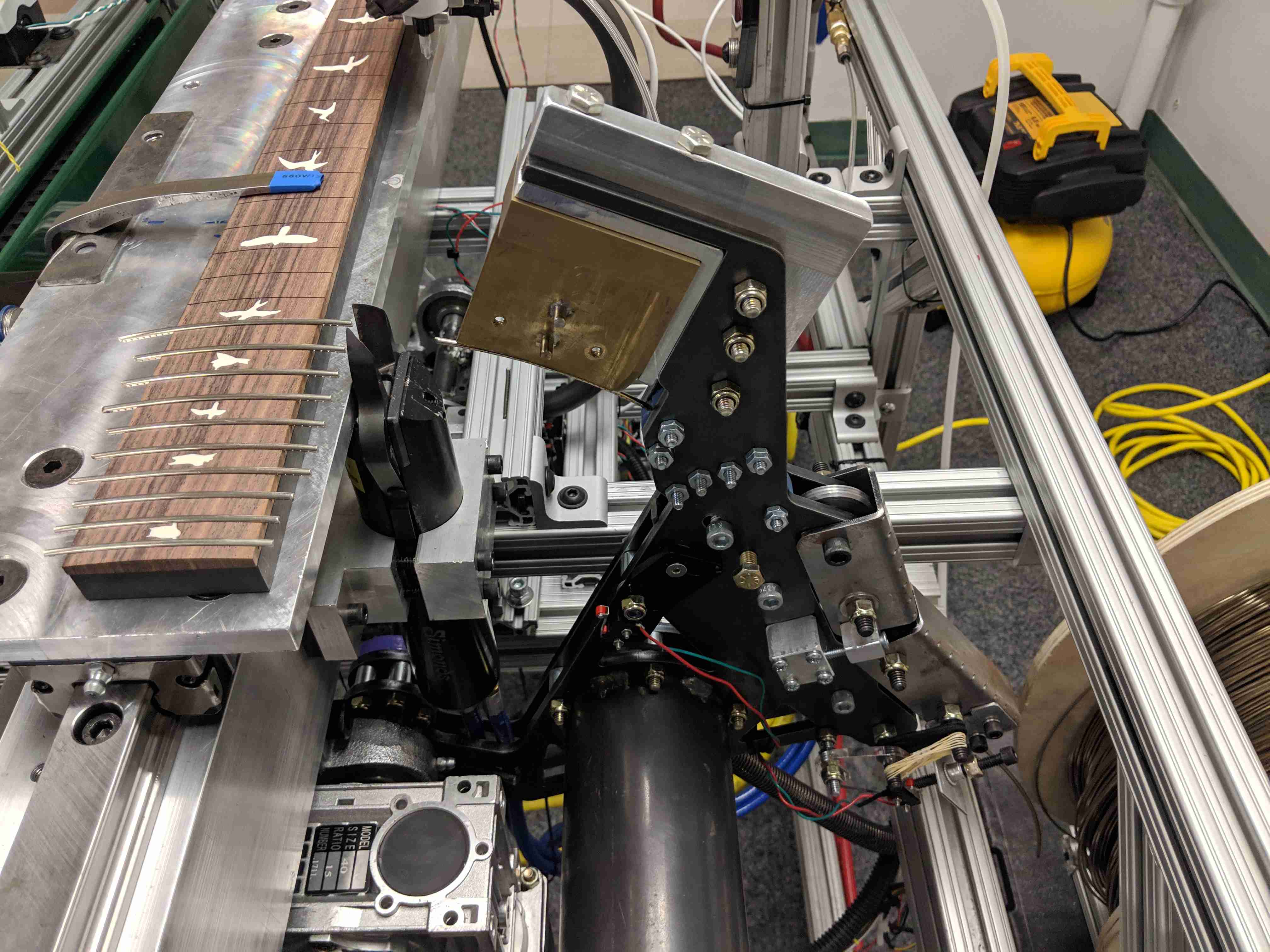
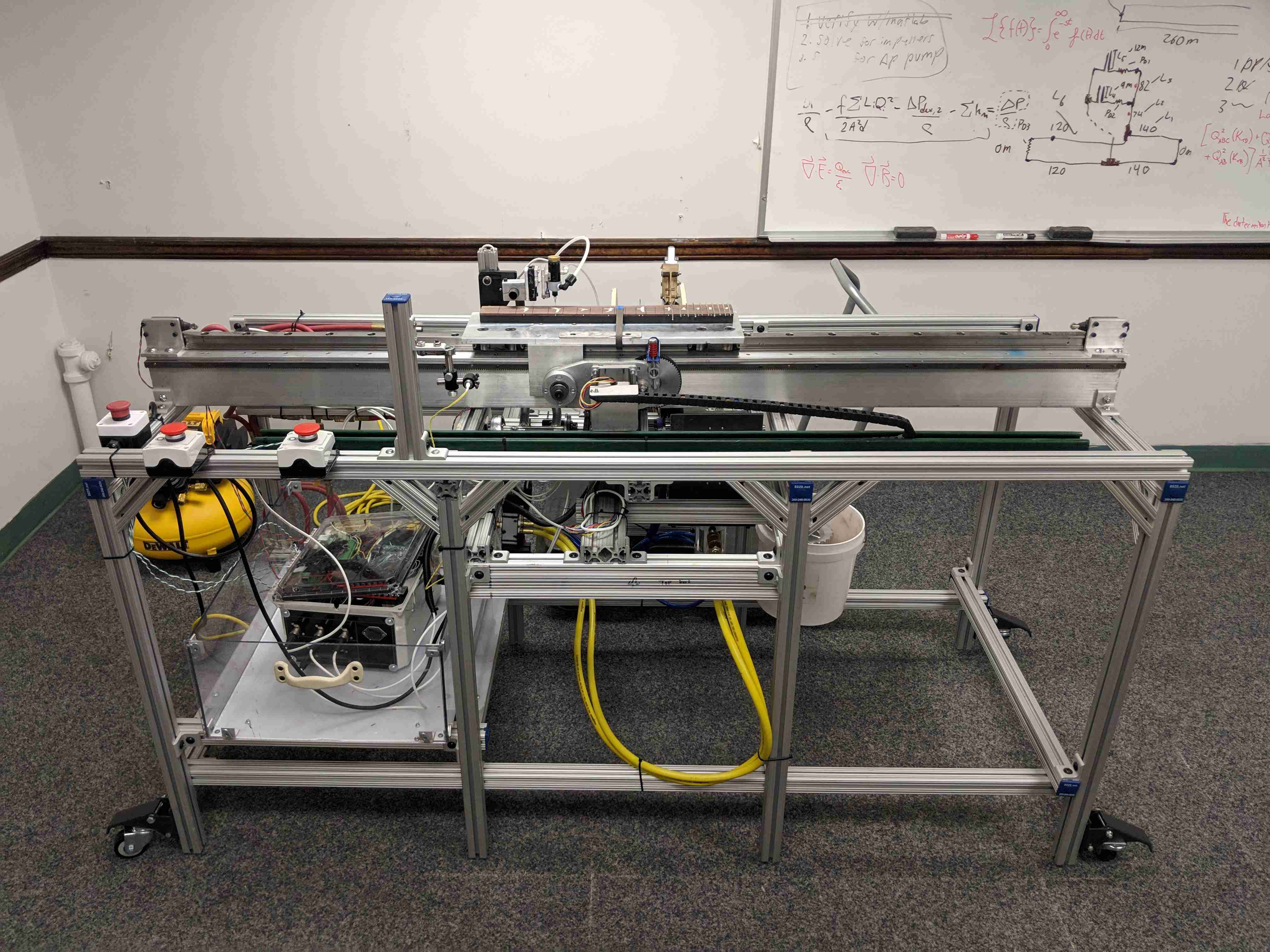

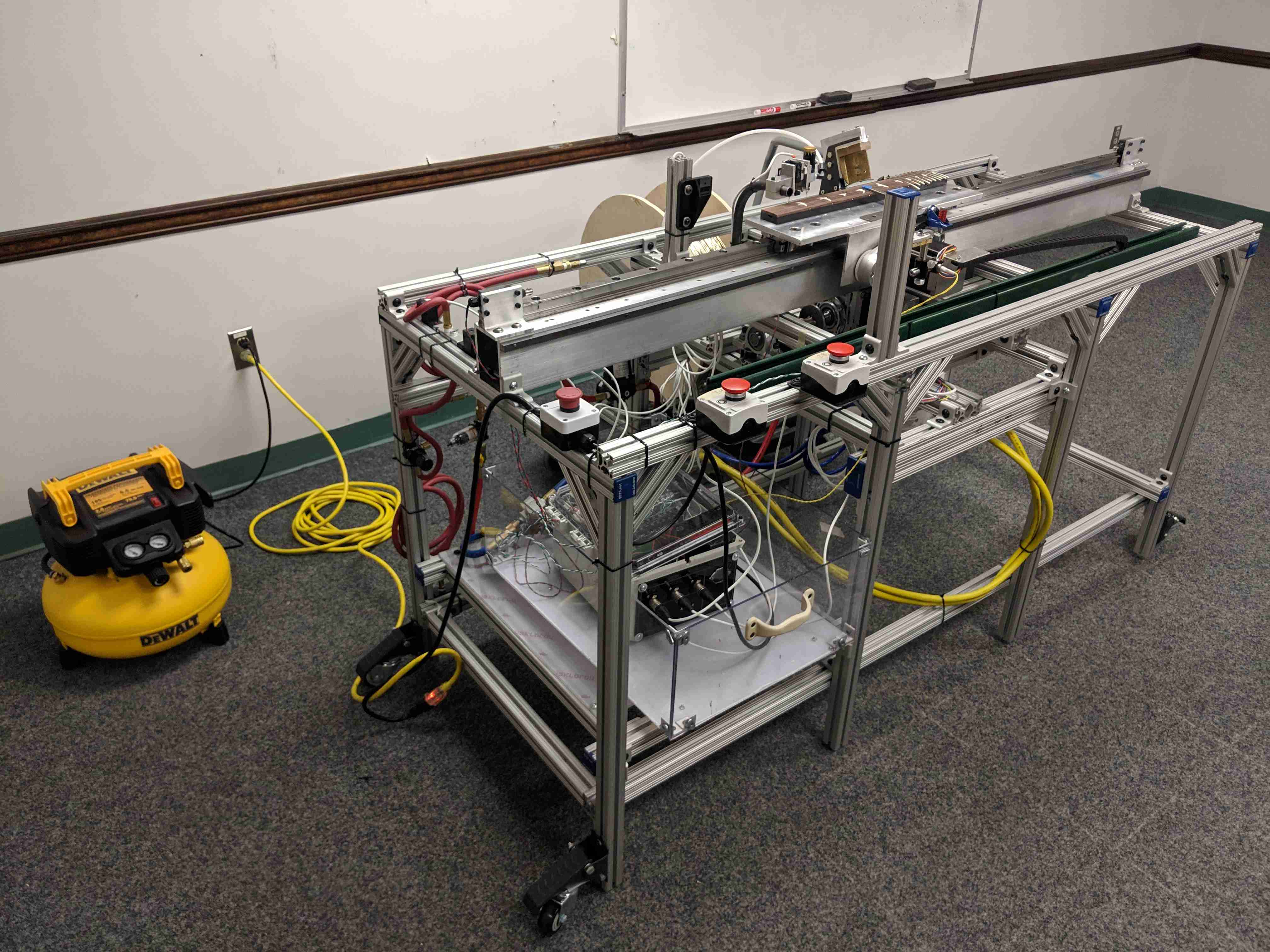







































Technical
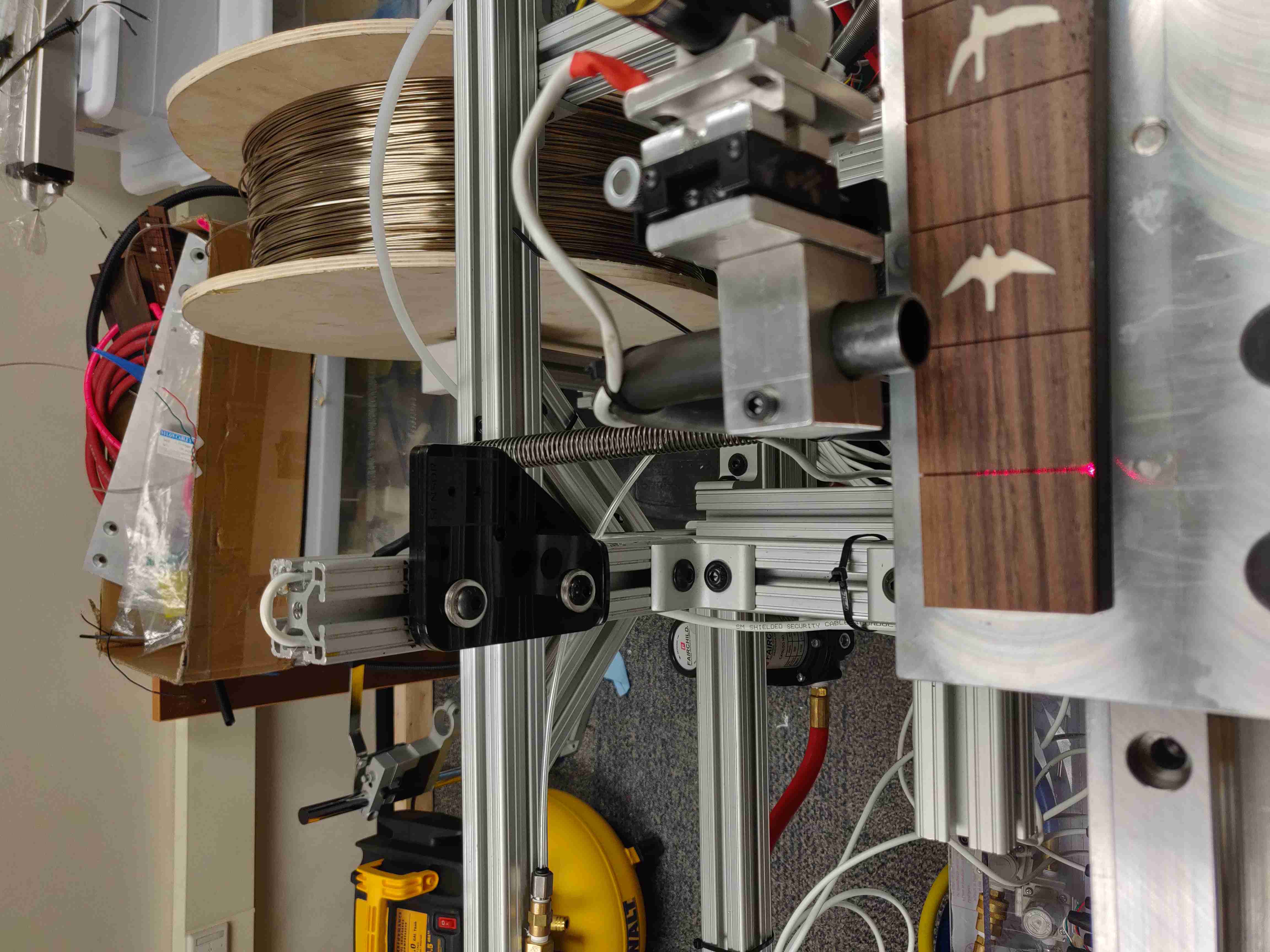
The main features of the robot include the sliding fret board platform, the glue arm, the presser mechanism, and the laser fret slot sensor. It is all controlled by a single Arduino Mega, which monitors the various sensors and controls the stepper motors and pneumatics. To press the frets, the robot performs the following steps:
- Measure the slot location by sliding the fret board in front of the laser
- Move the fret board to align the slot with the glue arm
- Swing the glue arm towards the fret board
- When the glue arm reaches the start of the fret board, activate the pneumatic valve to dispense glue
- When the glue arm reaches the end of the fret board, deactivate the glue valve
- Move the fret board so that the glue arm aligns with the next slot
- Repeat the glue process, reversing the motion of the glue arm, towards its original position
- Move the fret board so that the slot aligns with the press mechanism
- Swing the press mechanism over top of the fret board
- Activate the pneumatic dropping the press mechanism and fret wire into the slot
- Retract the press mechanism (this unspools fret wire for the next slot)
- Activate the pneumatics to close the snippers, and cut the fret wire
- Deactivate the pneumatics to open the snippers
- Repeat the above steps for the rest of the frets on the fret board
Software
To control the robot, I developed a C++ driver program, and a number of support modules. For development and debugging, the code makes extensive use of the Arduino's serial communication capabilities—keywords with optional parameters can be sent to the robot to instruct it to perform any of its possible operations (e.g. jog the fret board platform to a certain location, activate a specific pneumatic valve, measure the laser intensity, etc.). For normal operations, I wrote modules to provide convenient interfaces for each component of the robot, including low level components like stepper motors, limit switches, pneumatics, and also higher level components, like the glue arm, or presser subassemblies. To start the fret press sequence, an operator simply loads a fret board onto the robot, and then presses the two start buttons, kicking off a software sequence that runs each of the steps listed above for pressing frets.
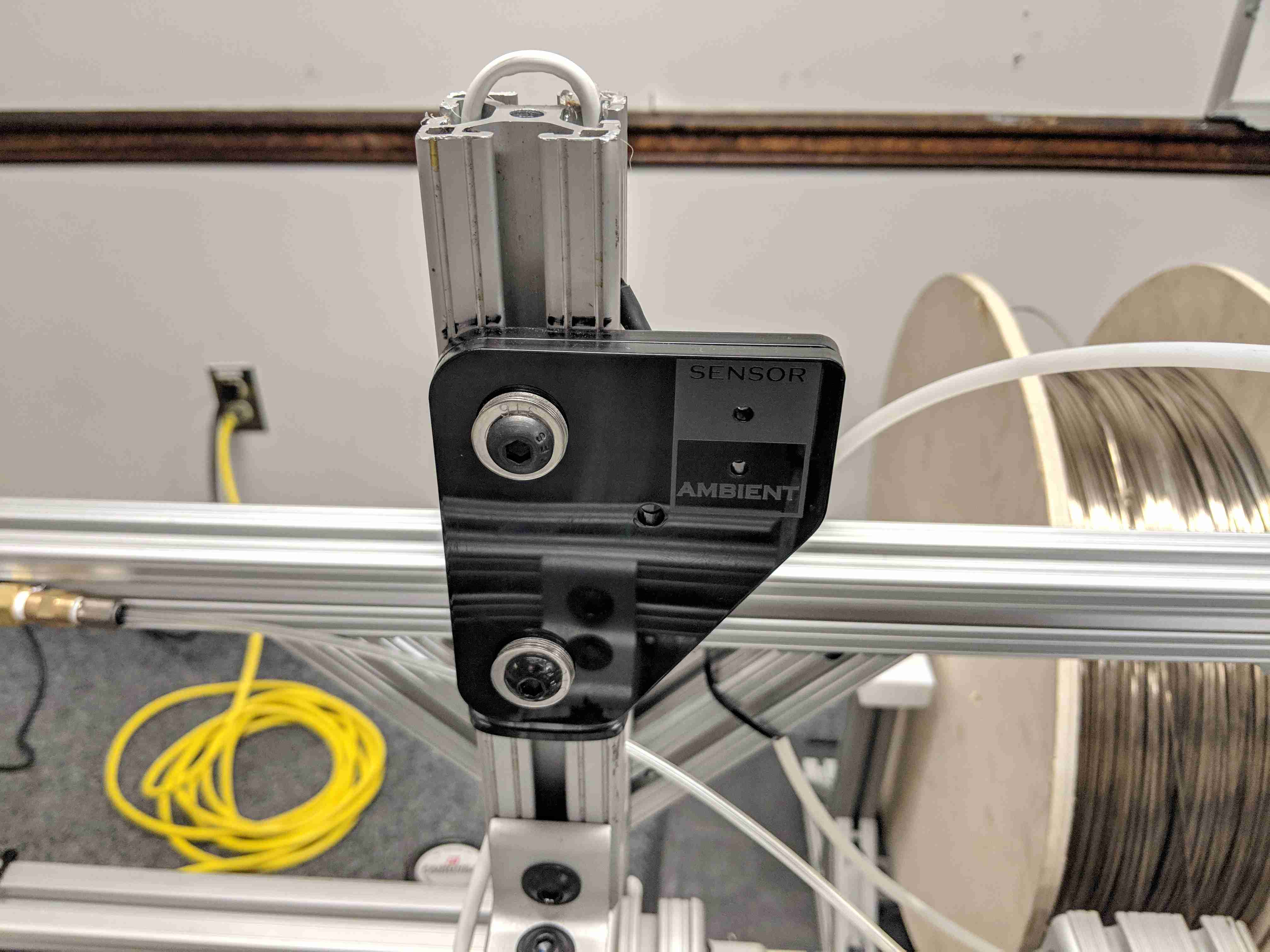
Laser Fret Detector
In addition to software work, I also helped develop solutions for several mechanical and electrical issues facing the project. In particular, I developed the laser system for accurately measuring the precise location of each fret on the fret board. The robot uses the fret locations to know where to move the fret board so that it exactly lines up with the glue arm, as well as the press mechanism. The detector works by shining a laser across the path of the fret board. As the board passes in front of the laser, it occludes the beam from the detector. When a slot passes in front of the beam, some of the laser light is allowed through, which is picked up by a photodiode on the other side of the machine. In software, the peaks in brightness are then correlated with the step count from the stepper motor, indicating precisely where each fret is relative to the robot.
Videos

Laser fret slot detection system
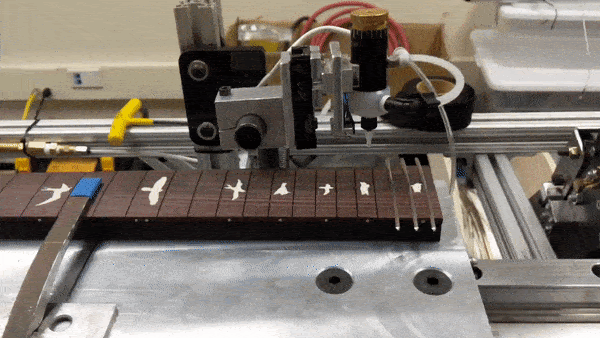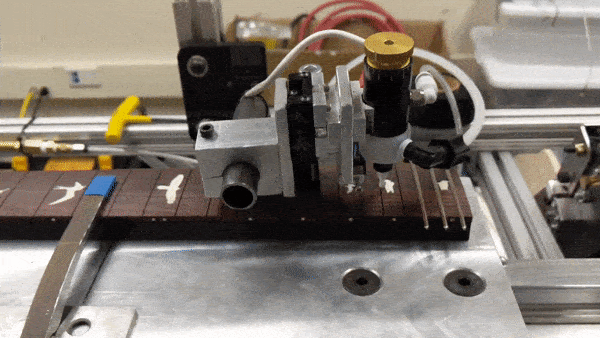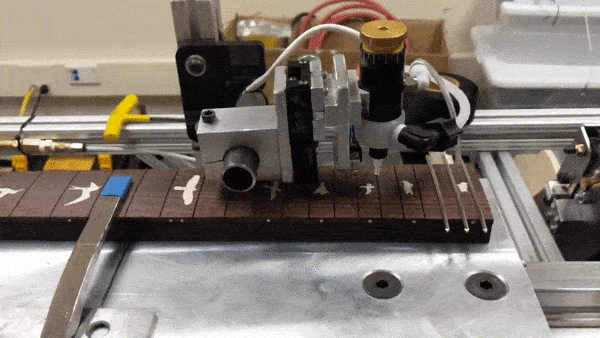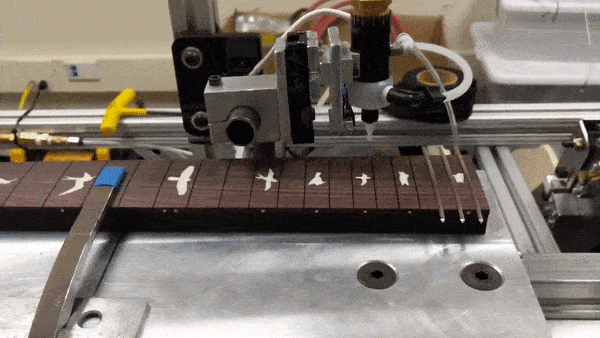
Glue dispensing mechanism
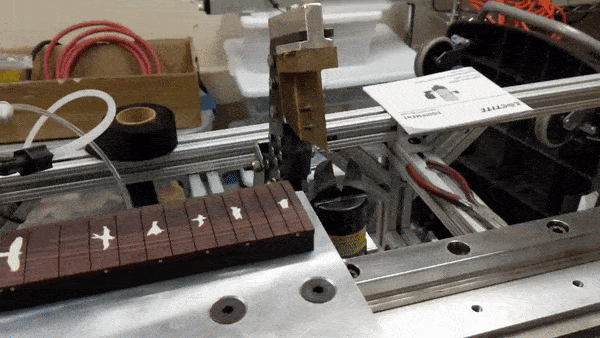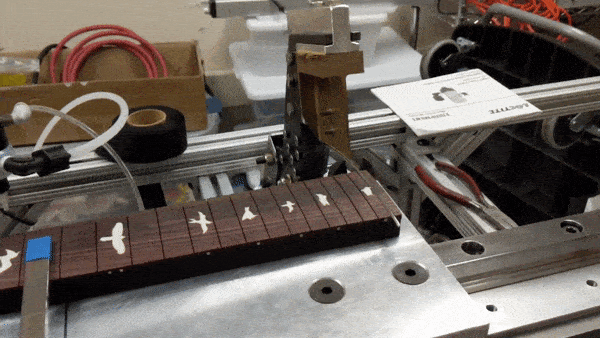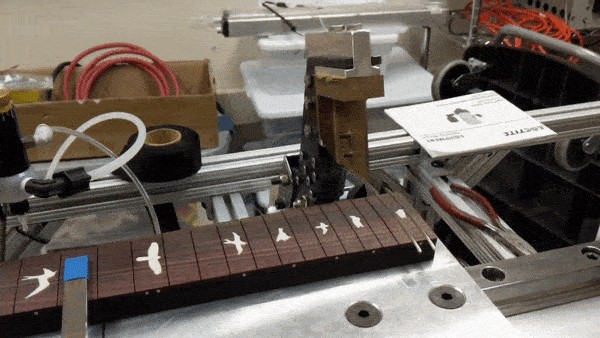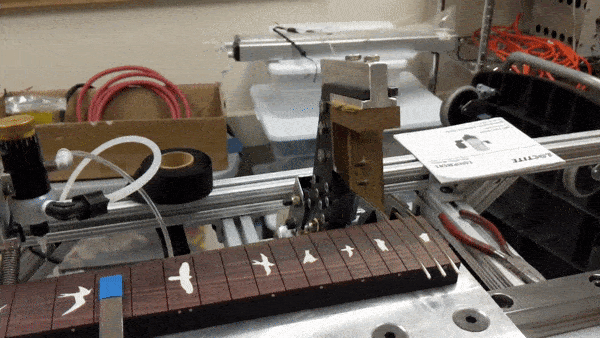
Fret press mechanism
